PPK on JavaScript: The DOM - Part 2/Page 5 | 2
[previous] [next]
PPK on JavaScript: The DOM - Part 3
Form fields
document.forms[] is equivalent to document.getElementsByTagName('form'). Apart from being able to access forms by name or id, there is little difference between these two nodeLists.
Every form has an elements[] nodeList. This is the one Level 0 DOM nodeList we still use often, because it has no counterpart in the Level 1 DOM and is so useful we cannot do without it.
document.forms[0].elements[] contains all form fields in the first form in the document. The trick is that these form fields can have different tag names (input, select, or textarea), so there is no single getElementsByTagName() call that delivers us all of them. Of course you can use three calls for the three tag names, but even then you don't get the form fields in the order they appear in the document—something that can be important in, for instance, form validation.
Form field properties
Every kind of form field has its own quirks, but before we discuss these we'll take a look at five properties any form field possesses: type, form, disabled, name, and value.
The type property of a form field gives its type: text, hidden, textarea, checkbox, radio, select-one, select-multiple, file, submit, or reset. It is possible to change the type of a form field, but this does not work in all browsers, and is counter-indicated.
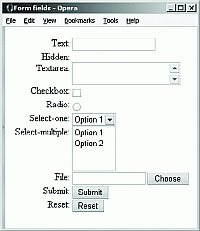
Figure 8.20 - Form fields
The form property of a form field refers to its parent form, and because the <form> tag is usually not the parentNode of a form field, this simple property can be quite useful, as we'll see when we discuss radio buttons.
The disabled property contains a boolean that says whether the form field is disabled (true) or not (false). You can set disabled, and this will disable the form field so that the user cannot change it. Note, however, that a disabled form field is not sent back to the server, even if it contains a value.
The last two properties are rather obvious: they give the name and the value of the form field.
This form field has name "test" and value "This is a test value". Of course the value is also the text contained in the form field, and if the user types a new text, the value changes. It is also possible to set the value:
The text in the form field is immediately updated. Changing the name of a form field is not possible in all browsers, and I advise against it.
text, hidden, and textarea
When you access a text field, hidden field, or textarea, you usually want to read out its value, which is contained in the value property.
checkboxes
Checkboxes have a value, too, but usually you want to know if the user has checked the box. This information can be found in the checked property, which gives a boolean true (checked) or false (not checked).
radios
Radios have a checked property, too, and it works the same as with checkboxes. Nonetheless, radios are slightly more complicated than checkboxes, because you usually need to go through an entire array of radio buttons and see which one of them is checked.
In order to work properly, all radio buttons that belong together should have the same name attribute. The Level 0 DOM conveniently creates a nodeList keyed to this name so that you can easily access a group of radio buttons.
Take this group:
They are accessible through this DOM call:
Now radios is a nodeList that contains all radio buttons with name="income" and you can loop through them to see if one of them is checked:
It's when you work with radio buttons that the form property of all form fields is very useful. Suppose you catch all click events on radio buttons and you want to go through all other radio buttons in the same group, just as we did above. Before you can do that, you have to gather the relevant radios:
First we determine which radio button is the event target, as discussed in 7F. Then we take all radio buttons in the same group by going to the form property of the target, i.e., the form it's part of (tg.form), and taking the radio button nodeList (tg.form[]) that's keyed to the name of the target (tg.form[tg.name]).
Remember that common select boxes have type 'select-one', not 'select'. This serves to distinguish them from multiple selects, which are never used.
Selects also have a value property, which takes the value of the selected option. Furthermore, they have a selectedIndex property that contains the number of the option the user has selected. Finally, they have an options[] nodeList that contains all options of the select.
options[] is a unique nodeList because you're allowed to add or remove elements, and these options are added to or removed from the visible select box. Therefore, options[] is not equal to getElementsByTagName('option'), which is a normal read-only Level 1 DOM nodeList.
Select Value In Older Browsers: Selects didn't have a value attribute in older browsers. Instead, to find the value of the selected option, you had to do this:
var sel = [the select box]; var value = sel.options[sel.selectedIndex].value;
You often see this syntax in older scripts, but nowadays it's not necessary.
In order to remove an option, simply set the correct element of the options[] nodeList to null:
Now the second option is removed from the select box, and of course all other options move one step up to accommodate this change. Therefore, a new x.options[1] is immediately available: this is the old x.options[2].
Adding an option is slightly more complicated. You must first create a new option object and add that to the options[] array:
Note that the new option requires two arguments: the text and the value. Once it's created, you insert it in the options[] array, and of course the old x.options[1] now becomes x.options[2], etc.
File uploads
File-upload fields are protected by JavaScript security. No script is allowed to enter a value in a file upload, since that could lead to a serious security risk:
No createElement(), No add()/remove(): Options should not be created by using createElement(), because Explorer doesn't support that. Explorer 5.0 even crashes when you try it.
The W3C DOM defines two methods, add() and remove(), to add and remove options, but since they work differently in different browsers you should avoid them.
If this were allowed, malicious site owners could easily download your password files or other system-critical files. Therefore, the only thing you can do with a file upload is read out its value.
Submit and reset
Submit and reset buttons that are <input> tags also have a value, which represents the text that's on the button:
<button> tags work differently: they contain a bit of text, and obviously this text is a separate text node as far as the W3C DOM is concerned. It is not accessible through the Level 0 DOM:
Example script
This script from Form Validation determines whether the user has entered anything in a required form field:
// Form Validation, lines 15-32
The script uses a switch() statement (see Section 5H) that uses the type of the field to determine which bit of code should be executed. If the required field is a text field, textarea, or select box, it must have a value. If it doesn't, the script returns false: required field not filled out.
Required checkboxes should be checked, while one radio of a required group should be checked. For checkboxes, the script simply returns the checked property, since that's true or false anyway. For radios, it goes through all radios in the same group (obj.form[obj.name]), and if one of them is checked it returns true, otherwise false.
[previous] [next]
URL:


 Find a programming school near you
Find a programming school near you