IE XML Data Island Functionality in NS6+ Browsers - Form Elements Overlapping a Styled Layer
IE XML Data Island Functionality in NS6+ Browsers
What does Direct Approach Mean?
Direct approach means to open an XML file directly in the browser, such as typing
the URL of the file in the browser's address/location bar.
NS and IE generation 6+ browsers have built-in style sheet processors that properly
display files with the *.XML file extension.
The best part which is to notice in the approach is that you can include an
XSL file in the XML document and the browser's XSL/XSLT processor will render
the XML document according to the imported XSL/XSLT file.
This is a powerful tool in the hands of web developers, allowing them to use XML for data display and data presentation.
To show you how it works, we need:
- An XML file.
- And an XSL file to set the page layout.
<xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<employees>
<employee>
<name>Joe</name>
<job>Programmer</job>
<department>Engineering</department>
<cubicle>5E</cubicle>
</employee>
<employee>
<name>Jane</name>
<job>Desigmer</job>
<department>Architecture</department>
<cubicle>12A</cubicle>
</employee>
</employees>
Next, we'll create a table using XSL and apply it to this XML file, which will
result in a table like the one below: 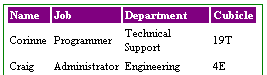
The difference between an ordinary XML file and one thats has XSLT file included, is one import statement, which might look like this:
<?xml-stylesheet href="DOMXMLParsing.xml" type="text/xsl" encoding="ISO=8859-1"?>
The rest of the XML document remains the same as the XSLT file contains processing
instructions to display the XML file in a given format. What is XSL?
XSL (Etensible Stylesheet Language) XSL has the capabilities to manipulate a document beyond the limits of CSS and is divided into 3 distinct parts:
- XSLT - This language is used to transform an XML document into almost any other document.
- XPath - This is an expression language used by XSLT to refer to or access any part of an XML document.
- XSLT - This is an XML vocabulary used to specify semantics for formatting (I used it few years back to convert XML documents to PDF file).
In this exercise, we'll use XSLT/XPath to transform XML data in to HTML which can be rendered on any web browser.
Note: There are XSLT processors out there that can spit HTML when fed XML and XSLT files - Xalan is one of them).
To learn more about XSL/XSLT, please visit the W3C XSLT pages, (it's the best resource you can find for free...:-).
Further discussion on XSL is beyond the scope of this article, so we forward
directly to actual example. Here, I've created an XSL file to display data in
a table. The XML file is named employee_xsl_db.xml and the XSL file included
in this XML file is named employee_db.xsl. Click
here to view.
Now, we're ready to write a detailed cross browser (IE5+ and NS6+) solution
that works perfectly.
Created: June 2, 2003
Revised: June 2, 2003
URL: https://webreference.com/programming/javascript/xml


 Find a programming school near you
Find a programming school near you